Table of Contents
You must have heard about GMAT a lot by now if you are a student who is planning to move abroad for studies. How much do you know about the GMAT test? Well, no matter how much you read about it you are still going to be left out on a lot considering the huge number of facets that the test has. Let me give you a comprehensive GMAT overview so that you don’t have to go anywhere else in the search for information. Let’s begin!
What is GMAT?
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is an essential aspect of the business school selection process. GMAT is a multi-choice, computer-based and computer-adapting structured exam that is also required globally for entry to graduate business programmes (MBAs).
GMAT is a structured exam that is approved by over 7,000 MBA and Master’s courses across 2300+ B-Schools and universities around the world. Various institutions put differing degrees of emphasis on standardised exams, such as GMAT, and utilise them along with other considerations such as GPA, class rank, community service, recommendations, and extracurricular events. The questionnaire is built on a computer-adaptive format that selects questions based on previous answers. The cumulative GMAT test score varies from 200 to 800 for the overall score. GMAT Scores are often provided for individual verbal, quantitative, analytical and integrated reasoning components.
The Quantitative Reasoning Section has fallen from 37 questions in 75 minutes to 31 questions in 62 minutes. The Verbal Reasoning Section reduced 36 questions in 65 minutes from 41 questions in 75 minutes. GMAC has chosen to reduce the average test period from 4 hours to 3.5 hours (including breaks and instructions) by reducing the number of unanswered questions used by examination research.
Curious to know what is going to be on the GMAT? Read the entire GMAT overview.
But before that, make sure to book yourself a free education loan counselling session by filling the form in this blog.
Overview of GMAT Syllabus and Eligibility | GMAT Components
The GMAT exam comprises four sections —Quantitative, Verbal, Integrated Reasoning, and AWA (Analytical Writing). Students are granted a total of around three and a half hours (with breaks) to complete the exam. Let us understand in more depth the GMAT overview.
Students will use the Choose Section Order to pick the desired test order. There are three choices available:
- Analytical Writing Assessment, Integrated Reason, Quantitative, Verbal
- Verbal, Quantitative, Integrated Reasoning, Analytical Writing Assessment
- Quantitative, Verbal, Integrated Reasoning, Analytical Writing Assessment
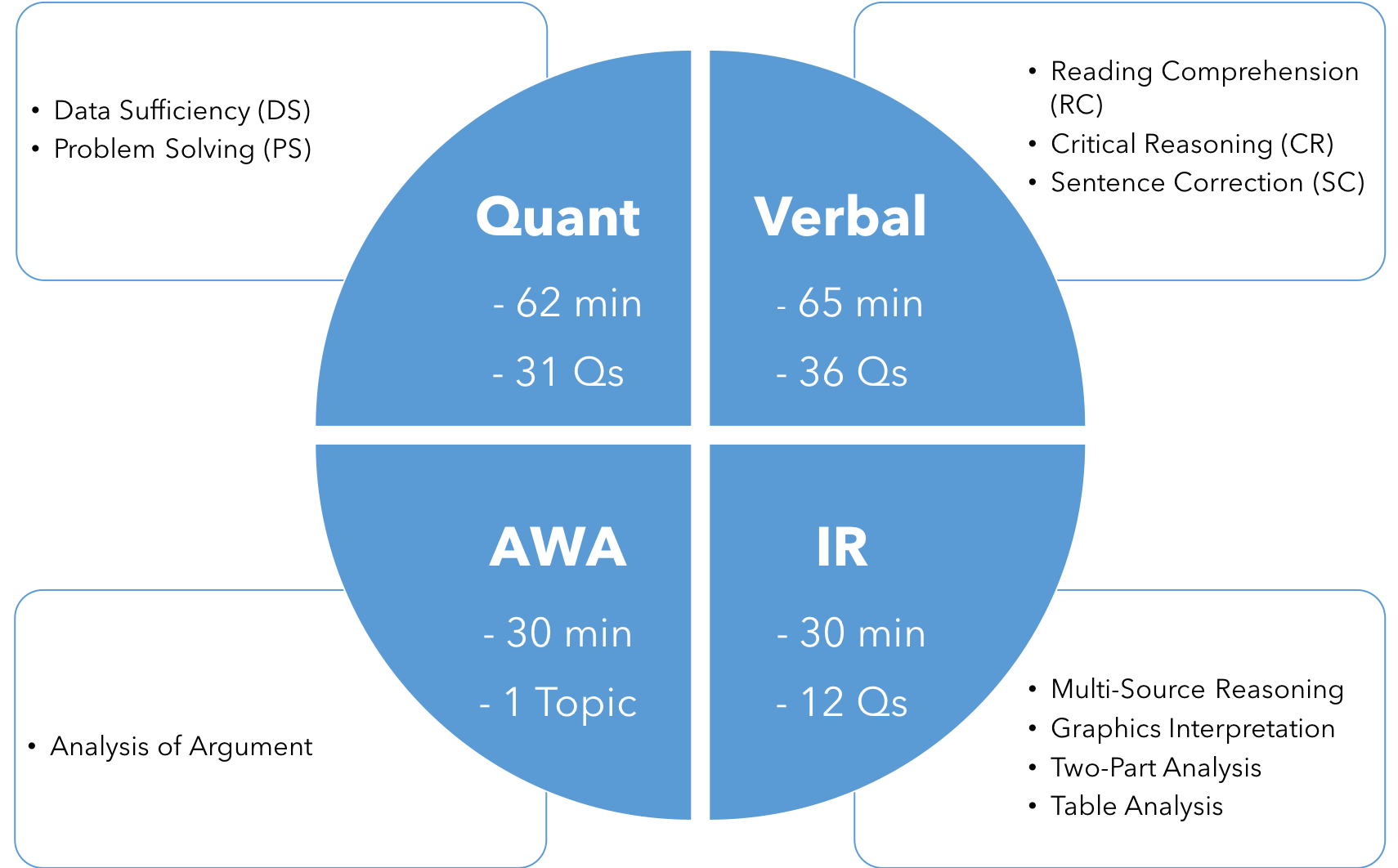
GMAT Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
The GMAT Analytical Writing Assessment, or “essay” section, lets business schools review writing skills. It is graded individually and one of the most important GMAT components. AWA performance is not used to calculate a score of 200–800. Tests are graded by a human grader and a machine scoring device, and the two grades are combined for the final score. If the marks are substantially different, so another person reads and grades the article.
Integrated Reasoning (IR)
The Integrated Reasoning section of the GMAT test measures how effectively one incorporates data to address difficult issues. For your target business schools involved in developing potential business executives, one of the most valuable qualities you will show is the willingness to take vast volumes of data to make rational choices.
- Synthesize facts in graphics, text, and number.
- Evaluate the related facts from a variety of outlets.
- Organize facts to see interactions and to address various, interrelated concerns.
- Combine and exploit facts from different channels to address complicated issues.
Quantitative
The GMAT Quantitative segment is structured to test the material and theoretical awareness of basic math principles, including arithmetic and numeric properties, algebra and geometry. The section consists of two types of questions. This is one of the most challenging GMAT components.
Verbal
The GMAT Verbal segment is structured to measure the mastery of standard written English, the capacity to analyse arguments, and the ability to interpret logically.
GMAT Overview
The GMAT exam assesses one’s mastery of basic arithmetic, algebra, geometry, multi-source data analysis, and grammar. More specifically, it tests the abilities to interpret and review written content, to think objectively and to solve problems. In the first place, the GMAT is a measure of logical thought abilities. Knowing how to reason and interpret facts is the secret to a successful GMAT ranking.
Overview of GMAT Registration
Before applying for the GMAT, one must grasp its criteria, its scheduling mechanism and the details pertaining to its fees.
The conditions of the GMAT test as follows:
- One must be at least 18 years of age. If you are a student between 13 and 17 years of age, you can take parental or legal guardian permission.
- The GMAT cannot be taken more than 5 times within 12 months.
- There must be a break of at least 16 days between doing the exam again.
One must not forget that the GMAT has no fixed test days, so plan one’s own test. It is recommended that students search their dream school to know their acceptance procedure as deadlines, and this will help them schedule their GMAT exam as well. It is advised that they enrol two or three months before the final test date so that students have the findings on time and can apply to their preferred university.
Overview of GMAT Fees
| Country | GMAT Registration Fees |
| UK | £225 |
| USA | $275 |
| India | INR18,122.42 |
| Eurozone | €250 |
| Non-Eurozone | $285 |
How is the GMAT Score Scale Averaged?
The GMAT score is made up of many separate numbers, each of which covers part of GMAT performance. The most commonly known number is the overall or composite GMAT ranking. This number varies from 200 to 800 in 10-point increments which are calculated by a mixture of the results in the Quantitative and Verbal portions of the exam. Business schools prefer to rely on the GMAT total ranking.
Ones Verbal and Quantitative sections are rated separately. Students will obtain a score of 0 to 60 for each section. Scores below 8 and above 51 are very uncommon.
The Integrated Reasoning segment is graded in 1-point intervals from 1 to 8. Questions have several sections, and one has to respond to each part correctly to get credit for the query. The Integrated Reasoning score is not counted in the total score.
The Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA) segment is ranked on a scale of 0 to 6 by two readers (one human and one computer). GMAC averages the two ratings to the nearest 1/2 point for the essay and rounds. The AWA GMAT overview performance does not contribute to one’s overall GMAT score.
The GMAT score will stay accurate for five years. If students have taken GMAT many times, GMAC will report all GMAT ratings over the last five years.
What is a Good GMAT Score?
When deciding the GMAT score target, it is often a smart practice to look at the mean or average GMAT score of the accepted applicants to the MBA programmes students are considering applying for. This is going to offer us a decent baseline. The performance Business Schools and MBA programs pay the most attention to the cumulative score scale of 200–800, with a mean value of 552.
Overview of GMAT Eligibility
- Minimum age limit: least 18 years.
*aspirants that fall in the age group of 13 to 17 are also allowed to attempt the exam if they have written approval or consent provided by legal guardians or parents.
- Basic understanding and fluency in English is a must for aspirants.
FAQs
1. What is the syllabus for GMAT?
GMAT is an international standardized test for admission to management schools. It is administered by the Educational Testing Service (ETS). The exam has four sections: Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA), Integrated Reasoning (IR), Quantitative section, and Verbal section. The AWA section is a 30-minute essay writing task that requires test takers to write an essay on a given topic. The IR section includes two 15-question sets: one on visual information and another on numerical data. In the Quantitative section, test takers are required to solve quantitative problems in different formats such as multiple choice questions, numeric entry questions, data sufficiency problems, etc. In the Verbal section, test takers are asked to read passages and answer questions based on them.
2. Who is eligible for the GMAT exam?
The eligibility criteria for GMAT is that one must be at least 18 years of age. If you are a student between the ages of 13 and 17, you may request permission from your parents or legal guardians to appear for the test.
3. How much is the GMAT exam fee?
The GMAT exam fee depends on which country you are appearing for the exam. The registration fee for GMAT in the UK is £225, in the USA $275, in India INR 18,122, in Eurozone €250, and Non-Eurozone is $285.
4. How many attempts are GMAT per year?
You cannot attempt the GMAT exam more than 5 times within 12 months. And between two GMAT attempts, there must be a break of at least 16 days. The GMAT exam has no fixed days, so one can plan to take the exam at any point during the year, depending on the university one wants to take admissions.
We hope that you are now familiar with the GMAT syllabus and eligibility along with the GMAT score scale. To prepare for GMAT, read: How To Prepare For GMAT And Ace The Test!










0 Comments